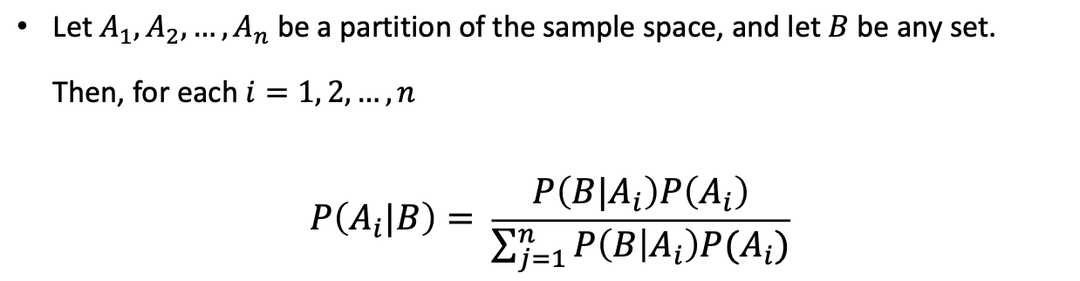Courses/통계적데이터분석
04_2 확률 (Probability)
noweahct
2025. 1. 22. 15:30
1) Probability
- an event occurring is defined as the long-run fraction of time that it would happen if the random process occurs over and over again under the same conditions
- The probability of an outcome 𝒆 in a sample space 𝑺 is a number 𝑷 between 0 and 1 that measures the likelihood that 𝒆 will occur on a single trial of the corresponding random experiment. The value 𝑷 = 𝟎 corresponds to the outcome 𝒆 being impossible and the value 𝑷 = 𝟏 corresponds to the outcome 𝒆 being certain.
- The probability of an event 𝑨 is the sum of the probabilities of the individual outcomes of which it is composed. It is denoted 𝑷(𝑨).
Sample Space & Events
- The sample space (𝑺) of a random phenomenon is a set of all possible outcomes of the random phenomenon.
- An event is a subset of the sample space.
- e.g., 동전을 세 번 던졌을 때 나오는 동전의 앞 뒤
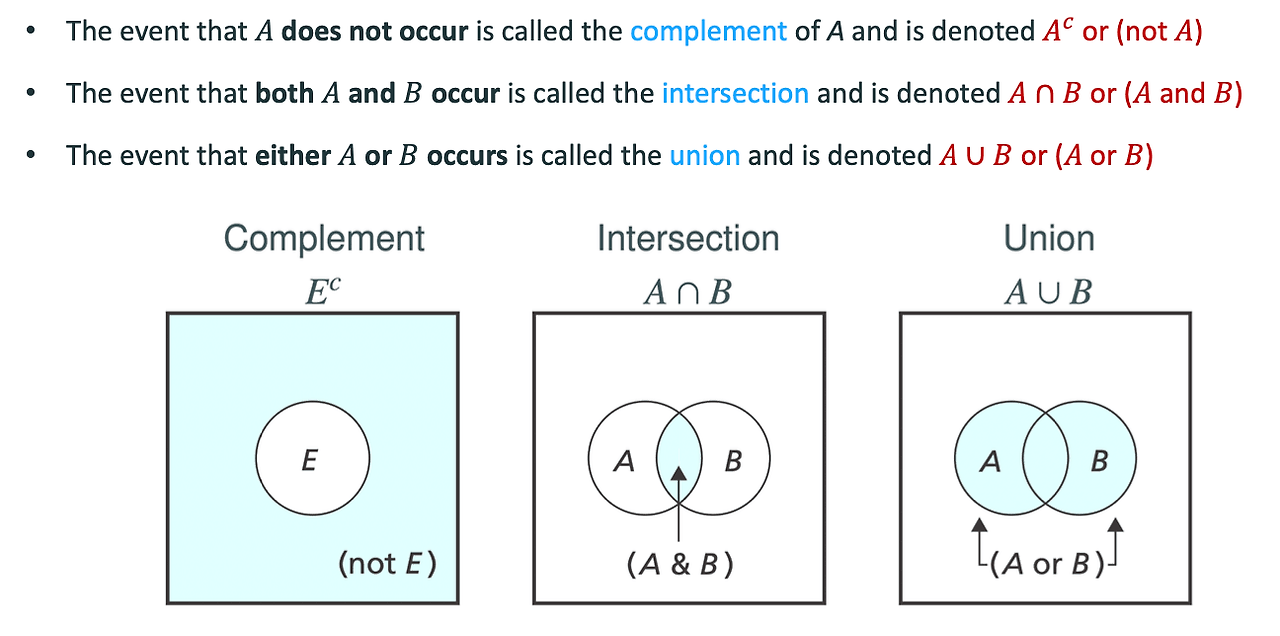
Intersections, Unions, and Complements
Disjoint Events (= Mutually Exclusive Events)

Addition Rule
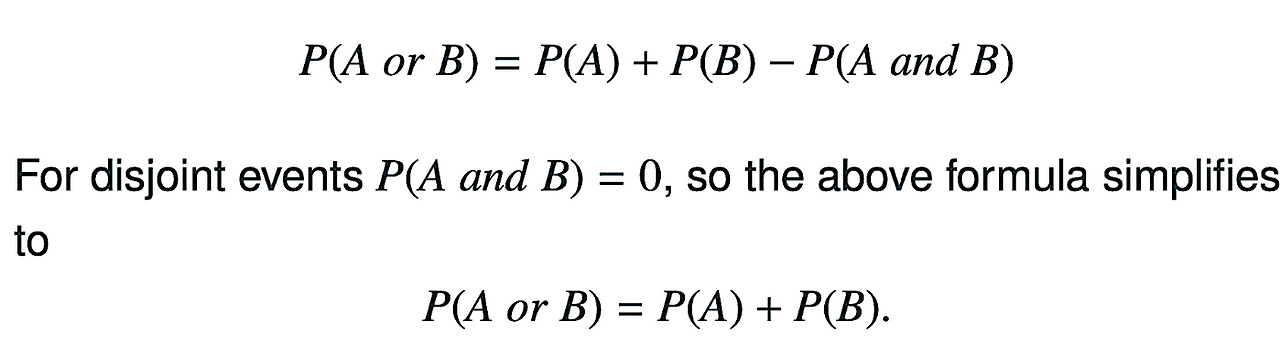
Complement Rule

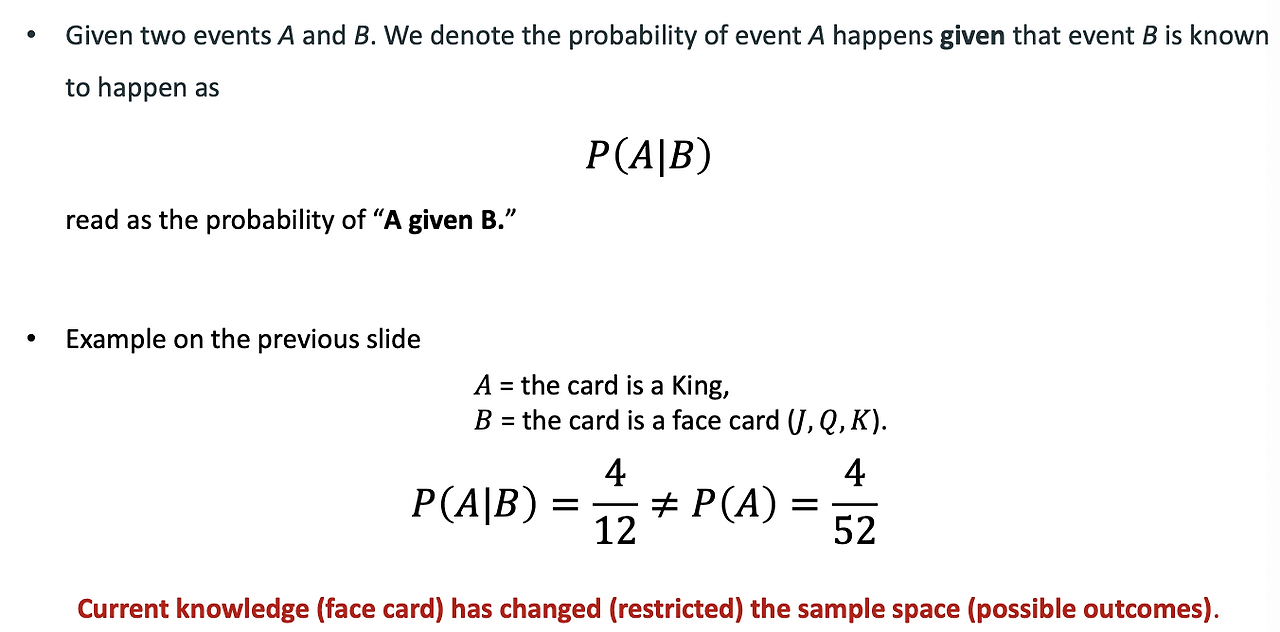
Conditional Probability(조건부 확률)
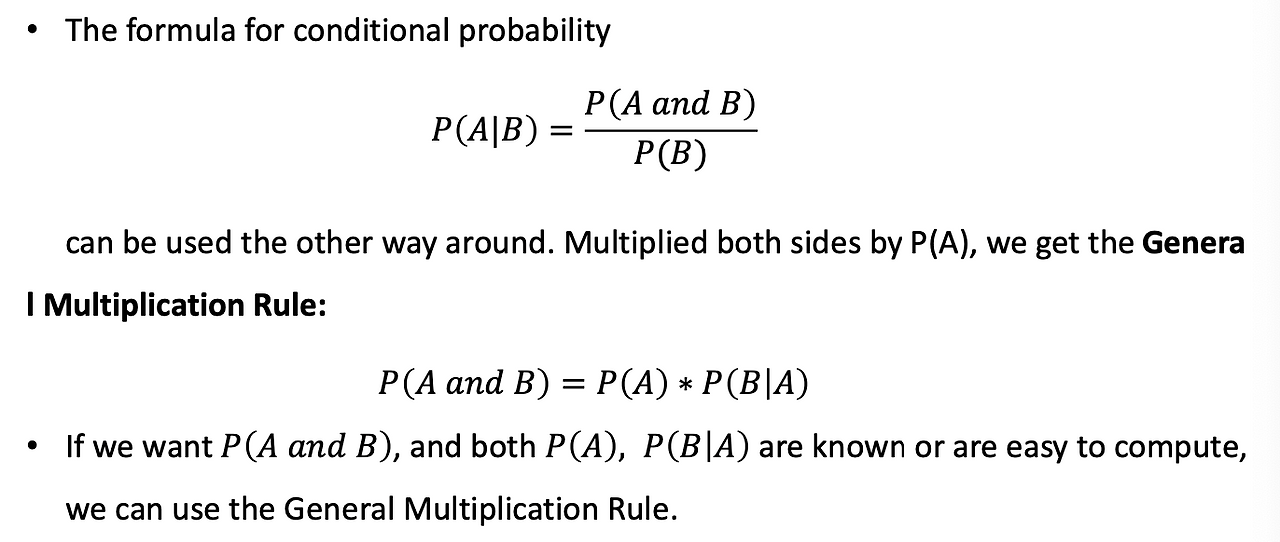
Multiplication Rule
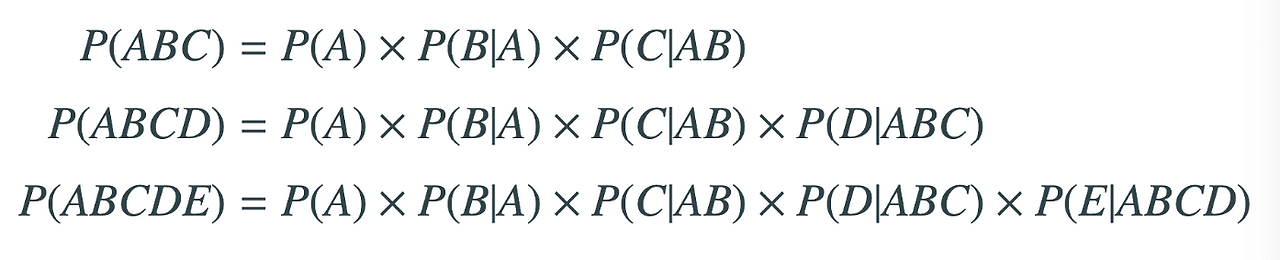
Independence
- Two random processes are independent if knowing the outcome of one provides no useful information about the outcome of the other.

- e.g.,

Multiplication Rule for Independent Events

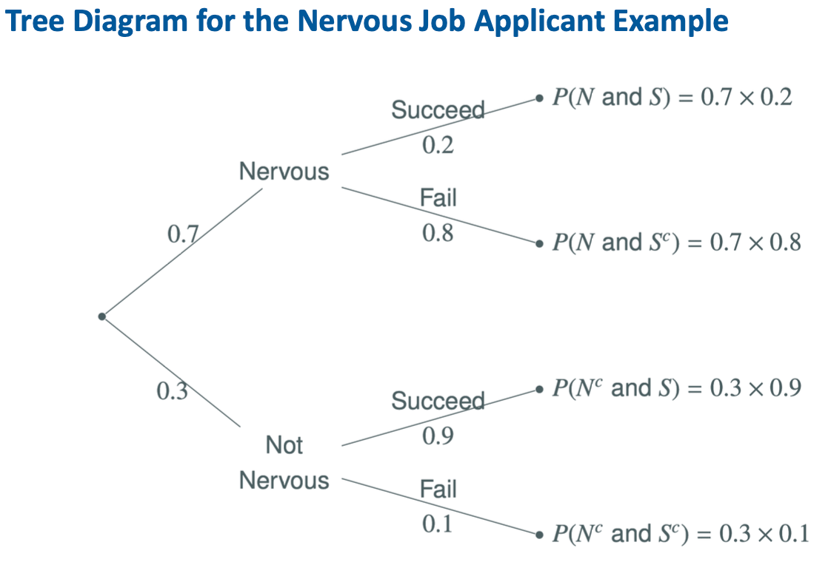
2) Tree diagrams and Bayes' Theorem
Bayes’ Theorem
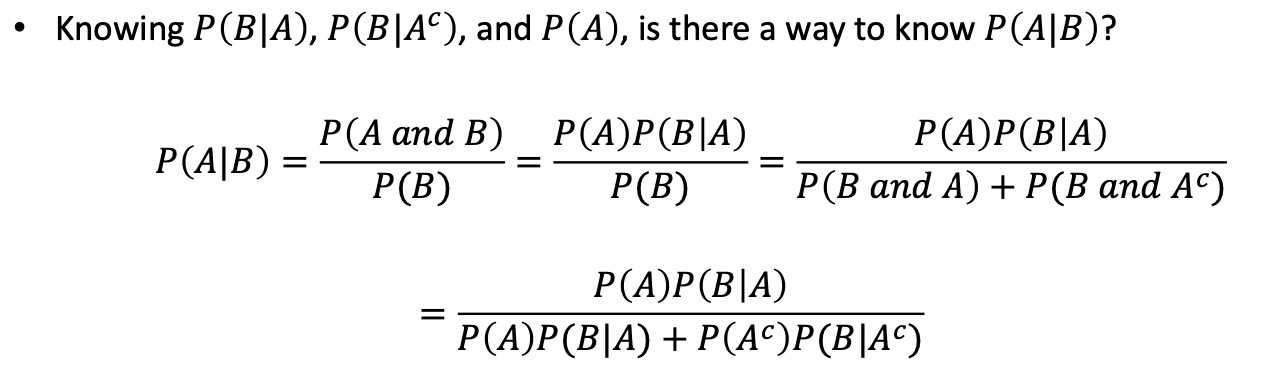
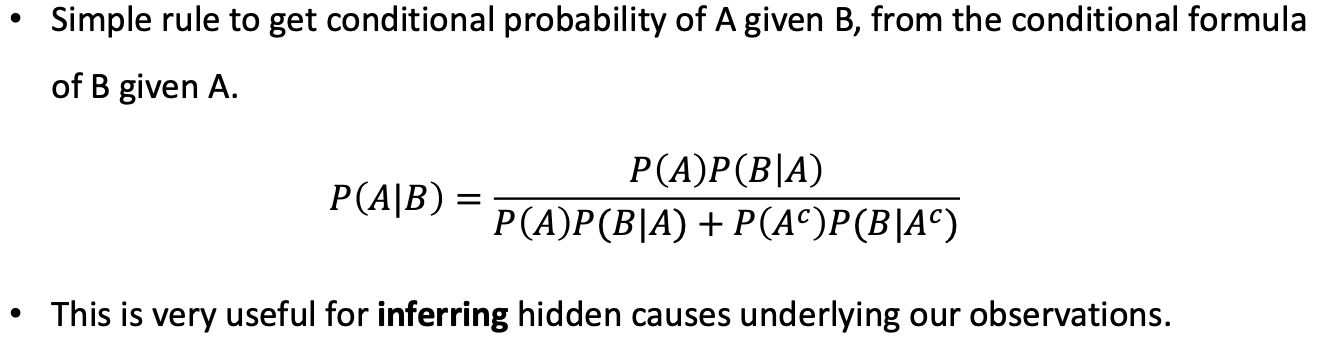

- 언제 사용하나?

Example of Bayes’ Theorem

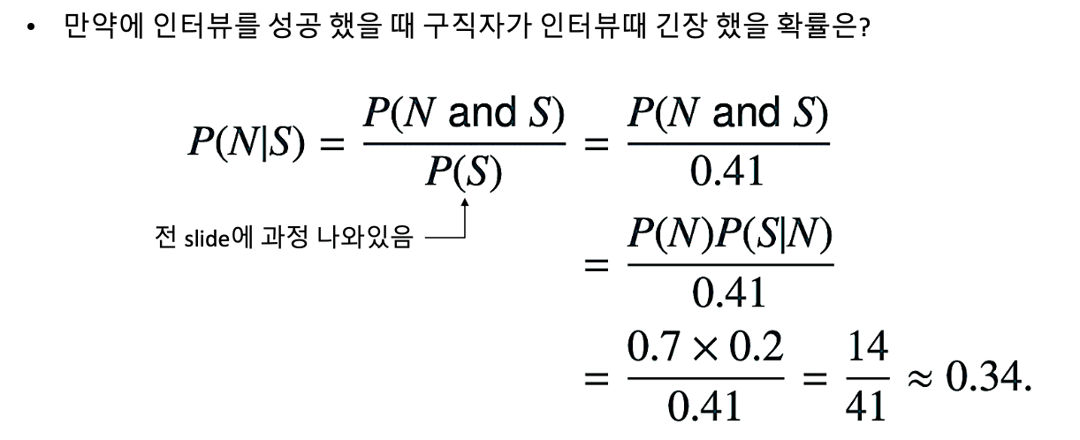
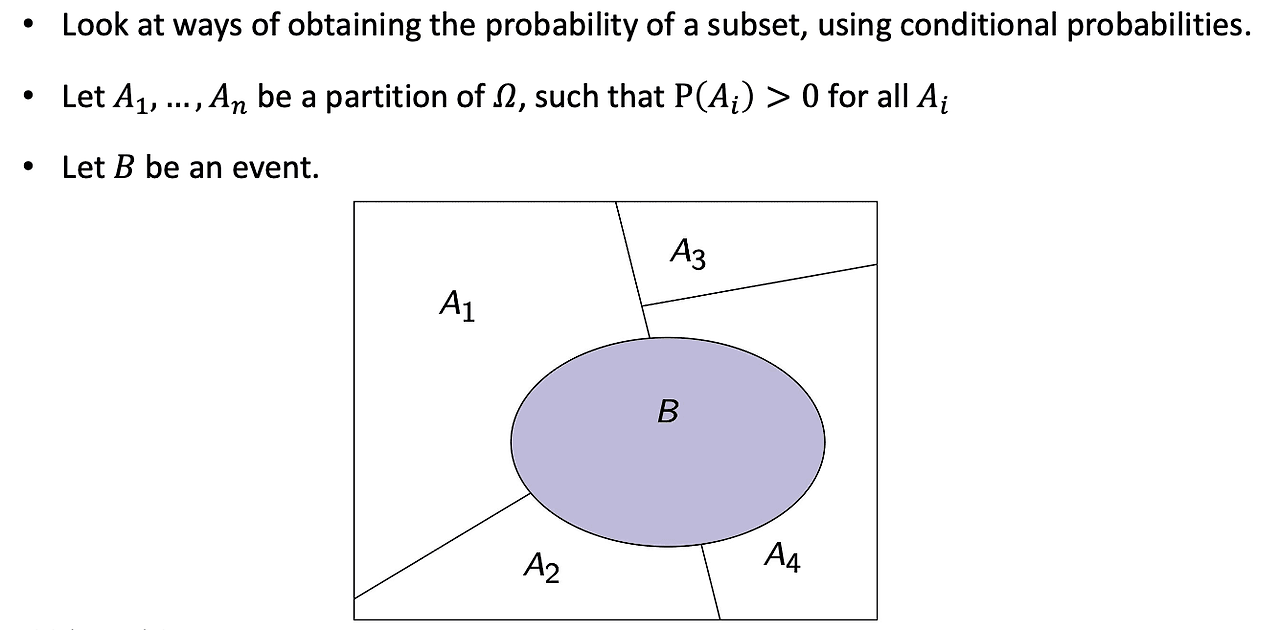
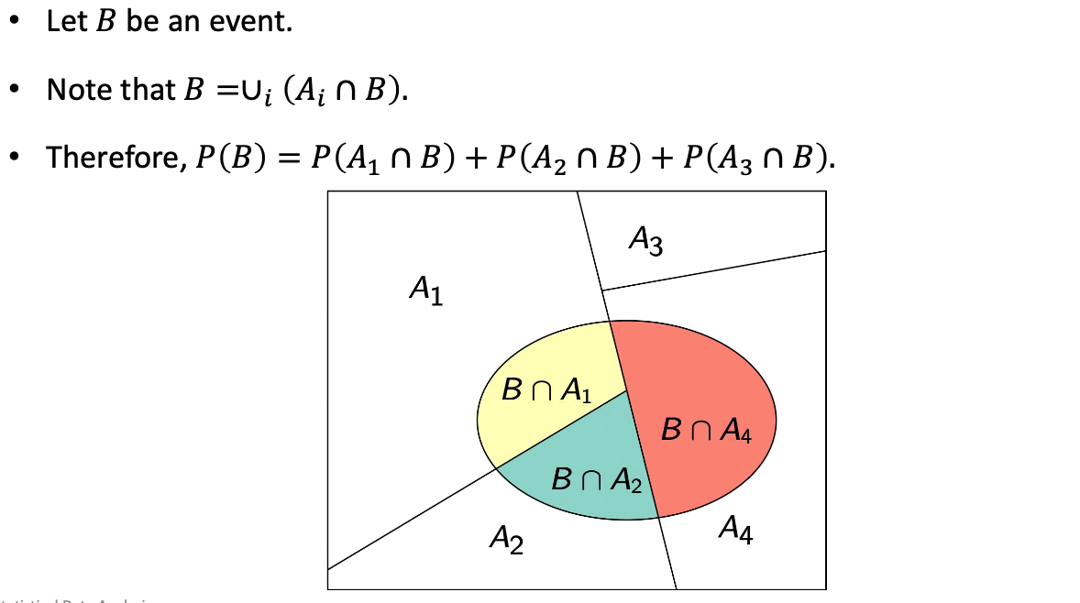
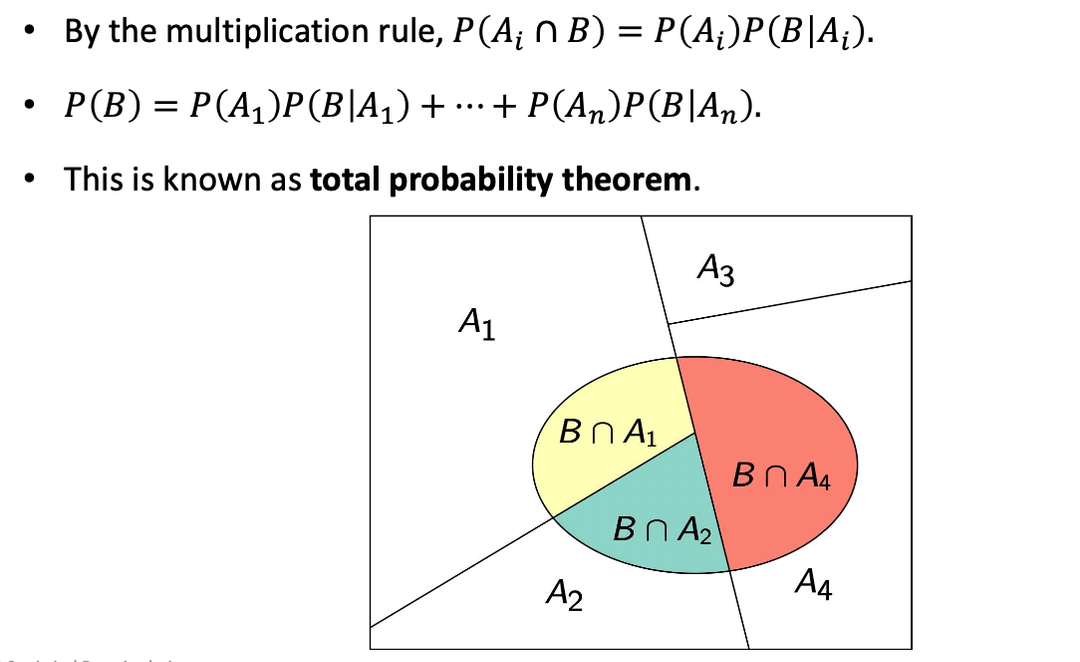
Total Probability Theorem